HTML Introduction
What is HTML?
HTML is a markup language for describing web documents (web pages).
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- A markup language is a set of markup tags
- HTML documents are described by HTML tags
- Each HTML tag describes different document content
HTML Example
A small HTML document:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
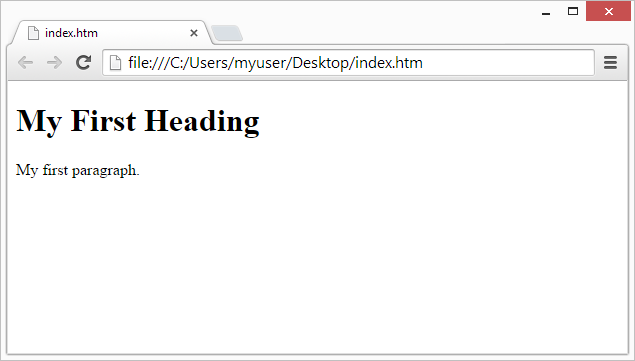
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Try it yourself »
Example Explained
- The DOCTYPE declaration defines the document type to be HTML
- The text between <html> and </html> describes an HTML document
- The text between <head> and </head> provides information about the document
- The text between <title> and </title> provides a title for the document
- The text between <body> and </body> describes the visible page content
- The text between <h1> and </h1> describes a heading
- The text between <p> and </p> describes a paragraph
Using this description, a web browser can display a document with a heading and a paragraph.
HTML Tags
HTML tags are keywords (tag names) surrounded by angle brackets:
- HTML tags normally come in pairs like <p> and </p>
- The first tag in a pair is the start tag, the second tag is the end tag
- The end tag is written like the start tag, but with a slash before the tag name
 |
The start tag is often called the opening tag. The end tag is often called the closing tag. |
|---|
Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, IE, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them.
The browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
HTML Page Structure
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
 |
Only the <body> area (the white area) is displayed by the browser. |
|---|
The <!DOCTYPE> Declaration
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration helps the browser to display a web page correctly.
There are different document types on the web.
To display a document correctly, the browser must know both type and version.
The doctype declaration is not case sensitive. All cases are acceptable:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<!doctype html>
<!Doctype Html>
Common Declarations
HTML5
<!DOCTYPE html>
HTML 4.01
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC
"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
XHTML 1.0
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
 |
All tutorials and examples at W3Schools use HTML5. |
|---|
HTML Versions
Since the early days of the web, there have been many versions of HTML:
| Version | Year |
|---|---|
| HTML | 1991 |
| HTML 2.0 | 1995 |
| HTML 3.2 | 1997 |
| HTML 4.01 | 1999 |
| XHTML | 2000 |
| HTML5 | 2014 |